אין מוצרים בסל קניות.
Basic Accounting Principles
A balance sheet liability account that reports amounts received in advance of being earned. For example, if a company receives $10,000 today to perform services in fundamental accounting the next accounting period, the $10,000 is unearned in this accounting period. It is deferred to the next accounting period by crediting a liability account such as Unearned Revenues. Next period (when it is earned) a journal entry will be made to debit the liability account and to credit a revenue account.

Course content
In the absence of a formal definition, it is best to start by understanding the term ‘dual aspect’. The dual aspect means that each party in a transaction is affected in two ways by the transaction and that every transaction gives rise to both a debit entry (Dr) and a credit entry (Cr). Equally, preparers should not be ‘overly prudent’ to the extent that they pick the lowest possible https://skyevia.co.uk/?p=14108 outcome simply to avoid the risk of overstating assets and income or understating liabilities and expenses. This would still not provide a fair presentation of the financial position or financial performance of the entity and, therefore, it is important that caution is exercised to avoid this as well. Learning outcome A1 from the FA2 syllabus is related to ‘The key principles, concepts and characteristics of accounting’. In this form, it is easier to highlight the relationship between shareholder’s equity and debt (liabilities).
The Accounting Equation and How It Stays in Balance
The owner's interest is the value of total assets left after all liabilities to creditors and lenders are settled. It is decreased by withdrawals by owners (dividends in corporations) and expenses. A liability is considered current of they are payable within 12 months from the end of the accounting period, or within the company's normal operating cycle if the cycle exceeds 12 months.
- A software package such as TallyPrime can be utilized to store every transaction that takes place.
- As with all other OpenStax offerings, modularity is an area in which this textbook shines.
- Therefore, the firm will initially record the amount as a liability in the unearned revenue account.
- The first is that there is no legal differentiation between Andrea and her business.
Matching Concept
Hence, net realizable value is sometimes referred to as cash realizable value. The third sample transaction also occurs on December 2 when Joe contacts an insurance agent regarding insurance coverage for the vehicle Direct Delivery just purchased. The agent informs him that $1,200 will provide insurance protection for the next six months. Joe immediately What is bookkeeping writes a check for $1,200 and mails it to the insurance company. Then on the next line, the account to be credited is indented and the amount appears further to the right than the debit amount in the line above. Because, the electricity expense was for the month of March even if the bill has been received and paid in April.
The financial statements are prepared regularly because it helps them in the decision-making process, and no firm can wait for long to know its results. The normal interval for the preparation of the financial statements is one year. According to the Companies Act, 2013 and the Income Tax Act, an organization has to prepare its income statements annually.
- The balance sheet reports information as of a date (a point in time).
- Under the accrual method, revenues are reported or recognized on the company’s income statement for the period in which the revenues were earned.
- The normal interval for the preparation of the financial statements is one year.
- Hence, the books of accounts include the accounting records from the point of view of the business instead of the owner.
- When the advertising occurs the prepaid advertising is reduced and advertising expense is recorded.
- Insurance Expense, Wages Expense, Advertising Expense, Interest Expense are expenses matched with the period of time in the heading of the income statement.
Business entity
To start with you will learn about the fundamental difference between bookkeeping and accounting. In Week 1 you will also learn how the purpose of management accounting differs from that of financial accounting. In Week 2 you will gain some practical skills in numeracy, including learning about rearranging simple equations such as the accounting equation. In Week 3 you will gain knowledge and understanding of the fundamental concepts that underpin double-entry accounting.
- In other words, the company will be able to continue operating long enough to meet its obligations and commitments.
- Similarly, an organization should not record its increase in the market value of stock until it is sold.
- GAAP is working on standardizing and regulating accountability concepts, assumptions, and practices.
- Therefore, assets and liabilities of a business are the business's assets and liabilities, not the owner's.
- It also helps companies comply with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), while still adhering to regulations and laws.
For example, interest earned by a manufacturer on its investments is a nonoperating revenue. Interest earned by a bank is considered to be part of operating revenues. A company that sells goods will report its inventory at its cost, not at the sales value. In addition to complying with US GAAP, corporations with capital stock that is traded on a stock exchange must also comply with some additional rules and communication required by the U.S.
Module 5: Income Statement – Part 2
Financial statements prepared with the help of GAAP can be easily used by the external users of the accounts of a company. The cost principle requires a business to record transactions at their original cost. The cost is determined at the time the transaction is completed, and not adjusted if changes occur after that. This principle applies to all assets including things like land and equipment.

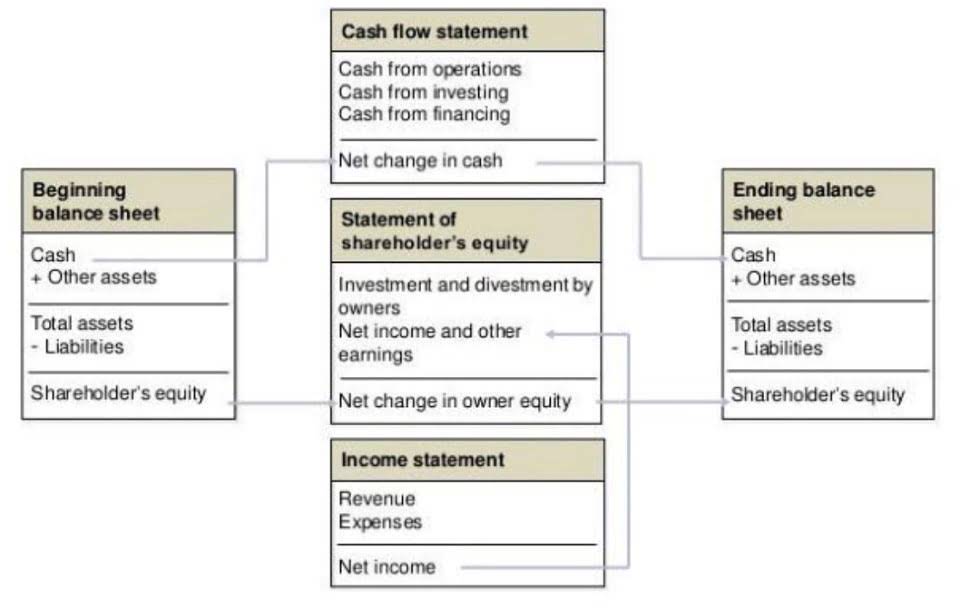
The account title for the money that Direct Delivery has a right to receive for having provided the service is Accounts Receivable (an asset account). If the company is a corporation, the third section of a corporation’s balance sheet is Stockholders’ Equity. (If the company is a sole proprietorship, it is Owner’s Equity.) The amount of Stockholders’ Equity is the difference (or residual) of assets minus liabilities. Marilyn points out that an income statement will show how profitable Direct Delivery has been during the time interval shown in the statement’s heading.
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. Fees earned from providing services and the amounts of merchandise sold. Under the accrual basis of accounting, revenues are recorded at the time of delivering the service or the merchandise, even if cash is not received at the time of delivery.


